
Almost any domain / business today is being transformed through SMAC. SMAC is a collective term referring to changes happening in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud. The impact of this change has been across the spectrum – Organizations, people and Products. In today’s article, we will enable you to take your analytics capabilities to next level by using Cloud computing.
We have explained the concept of cloud computing using R programming and RStudio using a step-wise methodology. Furthermore, you will also learn about the benefits of using R over cloud as compared to the traditional desktop or Local client / Server architecture.

Cloud computing has witnessed an unparalleled growth and penetration in last few years. It has enabled organizations to scale quickly and easily. Using cloud services, companies today collect, store and analyze huge amount of data, which was almost non-thinkable before. However, with services from the likes of Amazon, Google and Microsoft, cloud services are now accessible to any analyst.
Gone are the days, when you purchase a server for a particular capacity and then need to purchase a new one, when you grow out of the previous capacity. For example, most of the analysis I normally do is on a few GBs of data – sufficient to run on my laptop directly. However, recently Microsoft released ~400 GB of data about Malware and viruses on Kaggle. If, I would have thought of solving this problem on my laptop, I would have run out of my internet plan in just downloading the dataset. Analyzing it is a separate challenge in itself.
Even if I would have downloaded the dataset, the only way to do meaning computation through non-cloud way was by buying new machine – not a very practical solution. This is where cloud computing comes in picture!
Must Read: Step wise guide to learn R Programming
As discussed in the case study above, cloud is cheaper for handling big data than storage on local desktops, laptops or servers. Wait. Big Data? Yes! Big Data is an umbrella term that basically denotes data whose Volume and Variety and Velocity is larger than conventional data sources and which requires distributed computing like Hadoop and non-RDBMS storage like NoSQL databases.
Must Read: A beginner’s guide to use big data using MongoDB
According to the NIST definition of cloud computing,
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models.
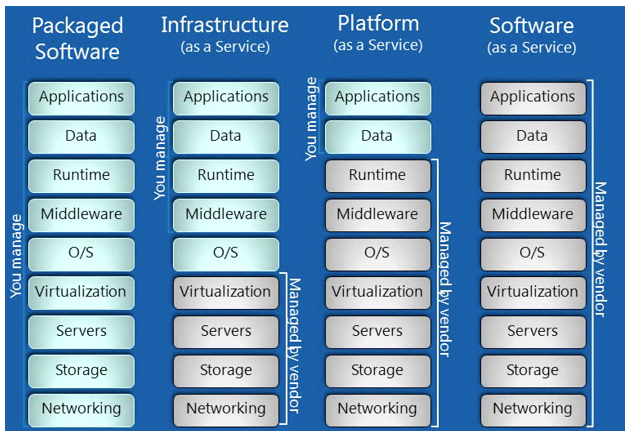
Cloud Computing consist of 3 components:
IaaS– To deploy their applications, cloud users install operating-system images and their application software on the cloud infrastructure. In this model, the cloud user patches and maintains the operating systems and the application software.
PaaS– Cloud providers deliver a computing platform, typically including operating system, programming language execution environment, database, and web server. Application developers can develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers
SaaS – In software as a service (SaaS), users are provided access to application software and databases. Cloud providers manage the infrastructure and platforms that run the applications. SaaS is sometimes referred to as “on-demand software”.
Python is free just like R, but the main reason R scores is that the statistical library of R packages is far more extensive. SAS remains the leading language for corporate analytics on the desktop but it remains expensive for small enterprises and has a significant disadvantage in capital expenditure commitment because of annual license structure instead of one time licence fee.
Must Read: A Quick Guide on SAS vs R vs Python
Take the Test: Should I become a Data Scientist?
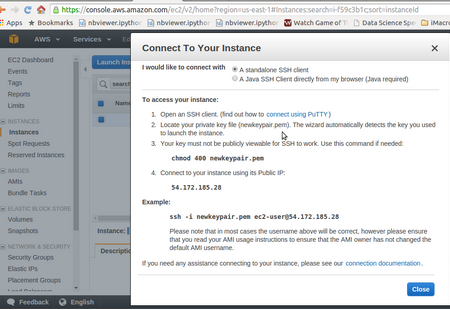
You can create a instance (a virtual machine that you access remotely) on Amazon Cloud, or on Microsoft Azure or on Google Cloud. You can then simply install R the same way as you use it on your local desktop. You connect to your remote machine through SSH or Remote Desktop.
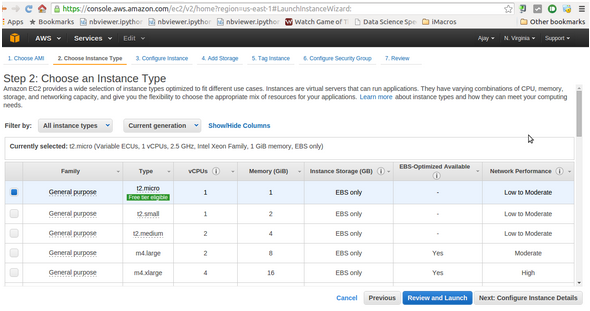
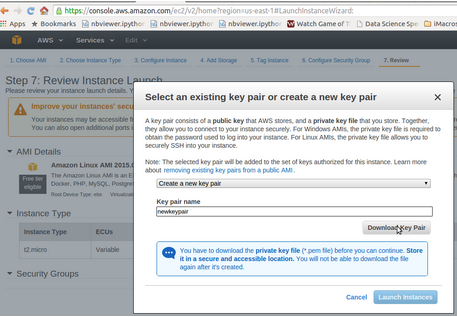
Here is a step by step process for creating a cloud instance on Amazon Web Services.
Note: Amazon has a free tier that enables you to try out the Amazon cloud for free for 1 year. However this is only for micro instances which have very small RAM and very small disk space. For higher RAM and higher storage you need to pay more. To look at the various instances and their per hour pricing you can see visit here. Basically fees is charged in compute units but this website makes it easy to figure out costs.

First you need to create your Amazon Id. Once you are done, follow the steps below to create a cloud instance on amazon web services:
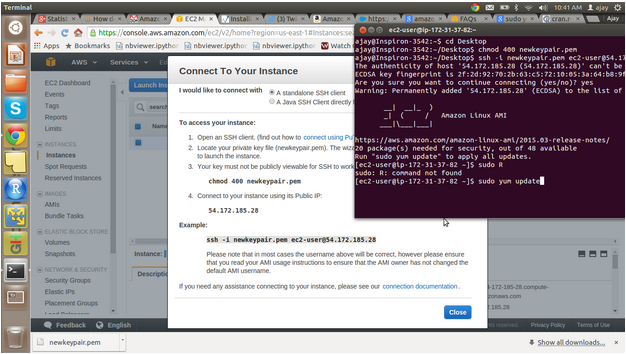
You can choose on demand instances, or even have reserved instances (booking a virtual machine for a fixed period of time and thus at a considerable discount).
Take the Test: Should I become a Data Scientist?
RStudio Server edition runs on only Linux. Therefore, we choose Linux instance on the cloud and then configure R Studio Server. We can then connect to the remote RStudio Server through the browser and use it just the same way.
Here is a step by step way to run RStudio on the cloud.
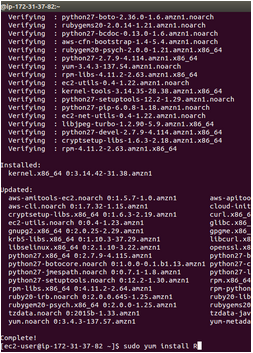
$ wget http://download2.rstudio.org/rstudio-server-rhel5-0.99.442-i686.rpm $ sudo yum install --nogpgcheck rstudio-server-rhel5-0.99.442-i686.rpm
$ sudo rstudio-server verify-installation

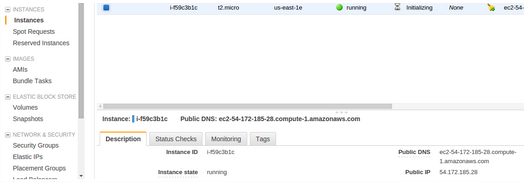
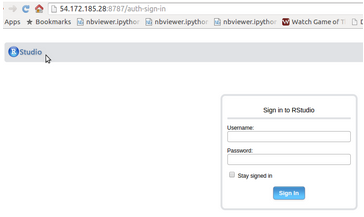
Bioconductor cloud is an amazing way of kickstarting R on the cloud. You can see the instructions here.
You can use cloud options from Google and Windows Azure as well. However most of the space is dominated by Amazon Web Services.
Yes we can use Azure Machine Learning with R on the cloud and also use Google Big Query with R.
Yes there are many examples. Resource 1 and Resource 2.